SERVICE
Graphite
Chemical composition of carbon, the crystal is hexagonal or trigonal natural mineral elements. It is the carbon in the diamond with polymorph variants. "Graphite" is used in 1789 by the AG Werner (AG Werner) according to the Greek word "Graphin" raised.
Outline Graphite was black iron to steel gray, shiny black streak, its chemical composition is carbon, But naturally occurring rarely pure graphite, often containing 10% to 30% of impurities, including SiO2, Al2O3, MgO, CaO, P2O5, CuO, V2O5, H2O, S, FeO and H, N, CO2, CH4 , NH3, etc. These impurities often occur in quartz, pyrite, carbonate minerals, clay minerals and bitumen being. A typical layered structure of graphite with its atoms arranged hexagonal columnar layer (top right), a covalent bond between the atoms - metal bond coupling. Places between layers molecular bond coupling. As compared with the interlayer covalent bond weak layers in parallel {0001} planes form a very complete cleavage. Carbon atoms in the structure according to the arrangement of space can be divided into 2H graphite-and 3R type two mineral types. ① 2H graphite. Layer of carbon atoms by AB, AB, AB, ...... order (repeat number 2) of the hexagonal structure, a hexagonal system. Its thermal performance and stability in a wide dynamic range (t> 2000 ℃, P <130kbar), widely distributed in nature. ② 3R graphite. Layer of carbon atoms by ABC, ABC, ABC, ...... (repeat number 3) arranged in diamond-type variant of the trigonal system, metastable phase, when the temperature rises to 2000 ℃ when that disappears in natural graphite can not be be individually isolated

Graphite crystal structure diagram
As with the structure of the graphite, so it is easy to expose along the {0001} plane as a sheet, and it has a hardness anisotropy in a direction perpendicular to the cleavage plane hardness of 5.5, the cleavage plane in the direction parallel to the hardness of 1 ~ 2. Graphite is soft, with a sense of fat and creamy, dyed hand, the relative density from 2.1 to 2.2, with a flexible, inelastic, high temperature, melting point 3652 ℃, boiling point 4200 ℃, about sublimation at 4500 ℃. Graphite crystal lattice memory in the easy movement of electrons that can pass current, and transfer between atoms in a heat wave, so the thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity, and even better than copper and aluminum. But graphitic carbon atoms in the crystalline lattice of closely spaced atomic layer thermal vibration resistance make it weaker, even in the ultra-high temperature conditions tend to adiabatic state.
Scaly graphite as a leaf-like shape and a small coefficient of friction, high adhesion, and thus has plasticity, a peelable, breathable, transparent sheet, with a diamond cutting tool can produce high-strength graphite is difficult to process.
Graphite at room temperature with good chemical stability, free from any acid, alkali and organic solvents erosion. However, at high temperatures the graphite come alive. ① 700 ℃ when it lost its temperature steam erosion. ② to 900 ℃, the carbon dioxide it has erosion. ③ at 400 ℃ for high temperature, the graphite fluoride in the gas stream for a long time, it will generate a gray solid substance CF. ④ In the high temperature graphite with nitric acid, sulfuric acid, perchloric acid and other strong oxidizing agent, the volume of the expanded graphite.
Deposit types can be divided into naturally occurring graphite flake graphite, crystalline vein (or fibrous, columnar) graphite and graphite Aphanitic categories. ① flake graphite. Flaky, hosted in the earlier ancient Cambrian metamorphic rocks, mostly regional metamorphic deposits, a small number of magmatic hydrothermal deposits. ② crystalline vein graphite. Veined or cystic accumulate body, along with limestone pegmatite distribution of the contact zone. ③ Aphanitic graphite. Usually in fine grains, located in low-grade metamorphic slate, shale, or consisting essentially of graphite rock. The latter two are in contact metamorphic deposits. Coal-bearing strata in the main Aphanitic graphite graphite flake graphite part sweetlips by magma intrusion seam is formed in contact metamorphism.
Industrial Use:Graphite is widely used as refractory, lubricating materials, chemical industry in a variety of carbon products and carbon products. Spectroscopically pure graphite is widely used as the silicon components and electronics industry silicon sintering temperature, conductivity, thermal conductivity material. Silicon agent colloidal graphite as the electron tube paint. Graphite can be used in the nuclear industry, aerospace industry and defense industry, and supplies of synthetic diamond production.
Distribution of resources Graphite deposits in the world are concentrated in the more than 10 countries. ① flake graphite is mainly distributed in the former Soviet Union, China, Madagascar and Germany. ② Aphanitic graphite mainly in North Korea, South Korea, the former Soviet Union, China, Austria, Mexico, the Czech Republic and Slovakia.
World coal-bearing strata in the origin of graphite resources ① Asia China, North Korea, South Korea, Japan and Russia, Siberia area; ② Europe, Austria, Czech Republic, Italy, Germany, the former Soviet Union and Switzerland; ③ Americas Mexico, Brazil and the United States ; ④ Africa Kenya; ⑤ South Wales, Australia has Australia and other regions. Among them, Chungbuk Korea, North Gyeongsang and Gangwon Kuliesike and Noginsk Russia, Austria, Styria, Sonora, Mexico is the world's coal resources, a major producer of graphite.
China graphite rich in resources, large reserves, range, high-grade ore. It is one of China has advantages of minerals in the world, occupies an important position. Among them, crystalline flake graphite concentrated in eastern Heilongjiang, Shandong, Liaoning and Inner Mongolia, southern, northern Shanxi three mineralized zones.
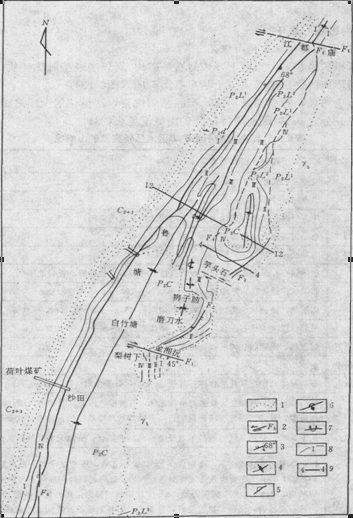
Chinese coal metamorphism graphite deposits in the eastern and western parts of the Pacific Rim region several magma fault, especially concentrated in the east of the Tan-Lu fault near its regions. Mainly in Hunan, Guangdong, Fujian, Beijing, Jilin and Heilongjiang provinces. Liaoning, Hebei, Jiangxi and other places are also in contact metamorphic graphite coal mines reported. Hunan and Jilin is China's important coal-bearing strata graphite mineral. Among them, Lu Tang amorphous graphite mine in Hunan and Jilin rock graphite mine is currently China's largest coal-bearing strata graphite ore mines.
Although graphite is widely distributed in the world as a non-metallic mineral resources, coal-bearing strata, however symbiosis with graphite deposit was more limited distribution. Although its metallogenic epoch extended from Carboniferous to Jurassic, but mainly Late Permian and Jurassic. In general, mainly in southern China in the Permian, Jurassic mostly to the north. Coal-bearing strata in Aphanitic graphite mine has a large scale, the characteristics of high grade ore. Due to thermal metamorphism, magmatism of varying intensity, certain areas or parts of the graphite mine, 3R graphite relatively enriched coal metamorphism become a major feature of the graphite deposit.
Reserves, according to 1987 statistics, the total amount of resources abroad graphite is estimated that about 0.7 ~ 0.8Gt.
By 1990, the world's coal-bearing strata in graphite reserves have been identified over 12.45Mt, of which more than 90% in China, the former Soviet Union, South Korea, Mexico and Austria.
China is the world's coal-bearing strata in the largest country of graphite resources, proven reserves 52.5164Mt, coal-bearing strata of the world's total reserves of graphite in more than 40%. Among them, the Hunan Lu Tong graphite mine production of amorphous graphite, natural high carbon content (generally 70% to 80%, up to 98%), the quality of the gifted not only ranks first in China, and is also one of the few; Jilin PANSHI graphite mine produced 3R graphite, is the production of color television picture tubes, graphite and synthetic diamond products such as fine quality raw materials
COPYRIGHT 2008-2013 Chenzhou Top Graphite Company Limited
